Master Data Management: A Key Pillar of Data Consolidation
In the ever-evolving landscape of data management, organizations are increasingly recognizing the pivotal role of Master Data Management (MDM) in achieving successful data consolidation. In this blog post, we'll delve into the significance of MDM as a key pillar supporting the seamless integration of data from diverse sources into a unified and reliable whole.
Unraveling Master Data Management (MDM)
Master Data Management is a comprehensive method of defining and managing the critical data shared across an organization. This often includes customer data, product information, employee records, and more. The objective of MDM is to provide processes for collecting, aggregating, matching, consolidating, quality-assuring, and distributing master data throughout an organization to ensure consistency and control.
The Role of MDM in Data Consolidation
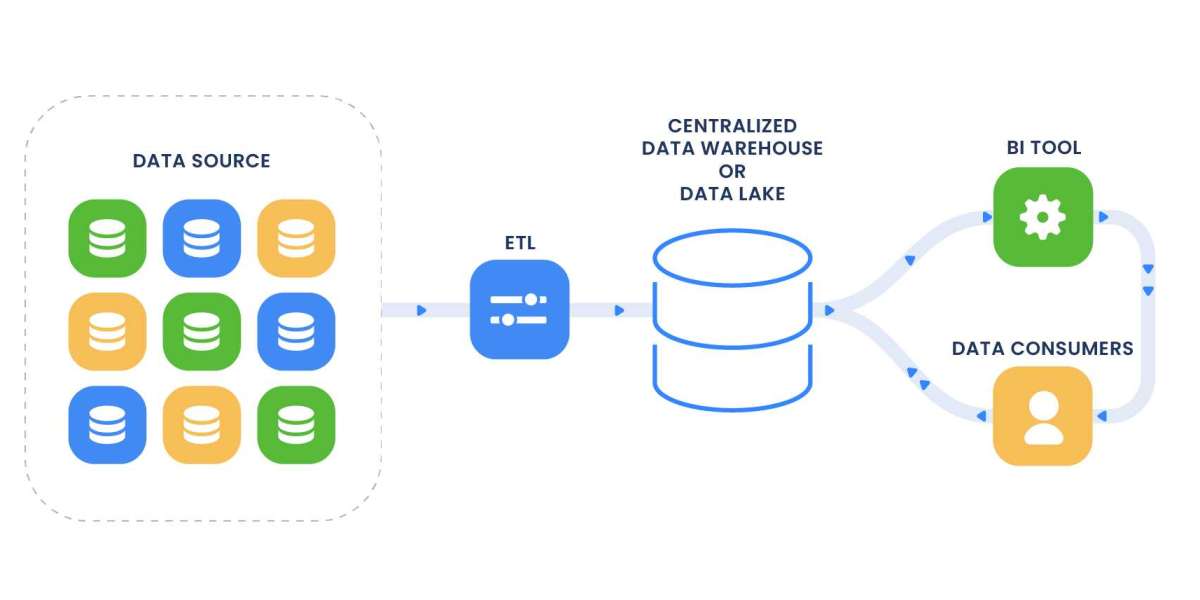
1. Single Source of Truth: MDM establishes a single, authoritative source for master data. In the context of data consolidation, this means creating a central repository for essential data elements. Whether it's customer names, product codes, or other key information, having a single source of truth eliminates discrepancies and fosters data integrity.
2. Consistency Across Systems: In organizations where data is stored in disparate systems and databases, maintaining consistency can be a challenge. MDM addresses this by synchronizing master data across various systems, ensuring that updates or changes are reflected uniformly.
Navigating Data Quality with MDM
1. Data Cleansing and Standardization: MDM involves data cleansing and standardization processes, which are integral to data consolidation. Inconsistent naming conventions, formatting variations, and other data quality issues are addressed to create a clean and standardized dataset.
2. Data Governance: MDM contributes to effective data governance by establishing policies and procedures for managing master data. This ensures that data is governed consistently across the organization, aligning with regulatory requirements and internal standards.
Implementing MDM for Successful Data Consolidation
1. Define Data Governance Policies: Establish clear data governance policies to guide the management and use of master data. This includes defining data ownership, access controls, and data quality standards.
2. Choose the Right MDM Tools: Selecting the appropriate MDM tools is crucial. These tools should align with the organization's data consolidation goals, offering features such as data matching, deduplication, and integration capabilities.
3. Ensure Stakeholder Engagement: MDM success relies on collaboration across departments. Engage stakeholders from various areas of the organization to ensure a comprehensive and inclusive approach to data consolidation. If you are looking for Data Consolidation services and Data Consolidation Tools services then probyto is the best company in the market.
Conclusion
In the complex world of data consolidation, Master Data Management emerges as a strategic enabler. By creating a centralized and standardized foundation for master data, organizations can overcome challenges and unlock the true potential of a unified, reliable, and comprehensive dataset. Stay tuned for more insights into the transformative power of data management in the evolving business landscape.