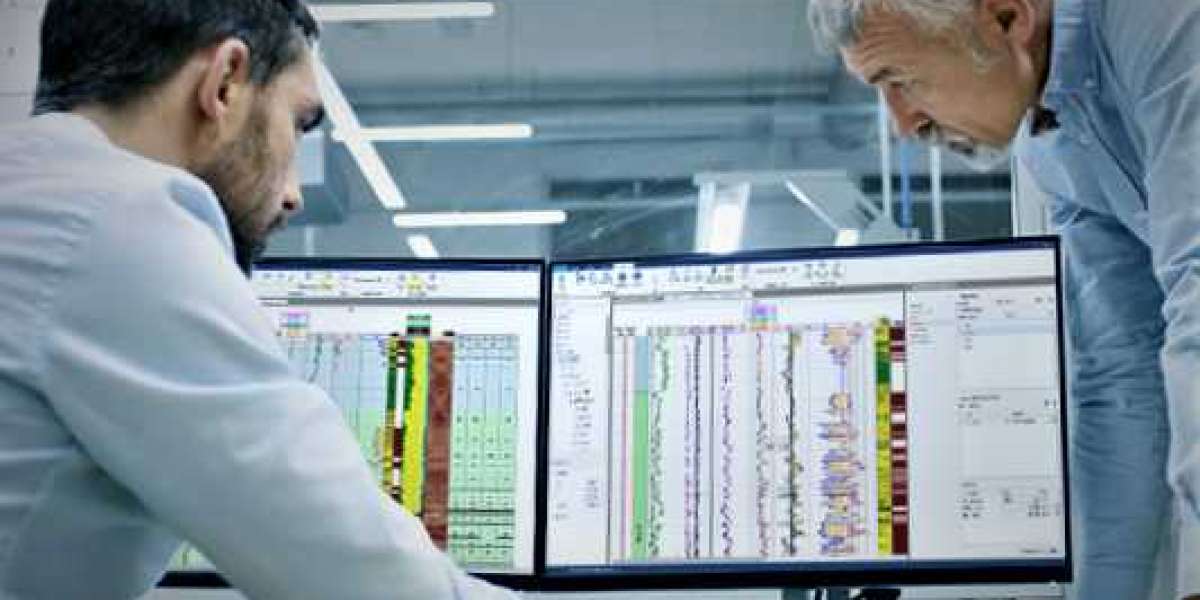
In the realm of petrophysics, a field that delves into the properties of rocks and fluids within the Earth's subsurface, the term "saturation height" holds a significant place. It's a concept that plays a crucial role in reservoir characterization and resource estimation. In this article, we'll unravel the intricacies of saturation height, its importance, and how it influences the exploration and extraction of valuable energy resources.
Defining Saturation Height
1. The Basics
Saturation height refers to the vertical distance within a reservoir rock where hydrocarbons (oil and gas) are present in sufficient quantities to be considered economically viable for extraction. This height is determined based on the saturation levels of the reservoir rock and the properties of the fluids it contains.
2. Fluid Saturation Levels
Fluid saturation levels within a reservoir rock are significant factors in determining saturation height. The rock contains a mixture of fluids, including water, oil, and gas. The proportion of each fluid type and how they distribute within the rock impact the saturation height.
Importance of Saturation Height
1. Reservoir Evaluation
Saturation height is a critical parameter used in reservoir evaluation. It provides insights into the vertical distribution of hydrocarbons, allowing reservoir engineers to estimate the potential volume of recoverable oil and gas.
2. Resource Estimation
Understanding saturation height aids in estimating the total amount of hydrocarbons that can be extracted from a reservoir. This estimation guides decision-making processes in the energy industry.
3. Production Strategy
Saturation height influences the production strategy for a reservoir. It helps determine where to place production wells and how to optimize extraction to maximize the recovery of hydrocarbons.
4. Economic Viability
Determining the saturation height contributes to assessing the economic viability of a reservoir. If the saturation height is within reachable depths and contains sufficient hydrocarbons, the reservoir is more likely to be economically feasible for development.
Factors Influencing Saturation Height
1. Rock Porosity
Porosity refers to the open spaces within a rock. Rocks with higher porosity tend to hold more fluids, affecting the saturation height.
2. Permeability
Permeability is the ability of a rock to transmit fluids. Rocks with high permeability allow fluids to flow more easily and can impact the saturation height.
3. Fluid Properties
The properties of the fluids present in the reservoir, such as viscosity and density, influence their distribution within the rock and, consequently, the saturation height.
Calculating Saturation Height
1. Log Analysis
Petrophysicists use well logs to analyze the properties of rocks and fluids within a reservoir. By interpreting these logs, they can estimate the saturation height.
2. Modeling Techniques
Advanced reservoir modeling techniques involve creating 3D models of the reservoir to simulate fluid behavior. These models help determine saturation height accurately.
Conclusion
Saturation height stands as a crucial factor in the field of petrophysics, guiding exploration and extraction efforts in the energy sector. By understanding the distribution of hydrocarbons within a reservoir rock, engineers and geologists can make informed decisions that impact resource estimation, production strategies, and economic viability. As the industry continues to evolve, the concept of saturation height remains a fundamental pillar of successful reservoir management.