Be cautious with personal information: Avoid sharing sensitive information like your social security number, bank account details, or credit card information unless you trust the website or recipient. Legitimate organizations will rarely ask for such information through email or social media.
Use strong, unique passwords: Create strong passwords for all your online accounts and avoid using the same password across multiple platforms. Consider using a reliable password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Whenever possible, enable 2FA on your accounts. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification step, such as a unique code sent to your mobile device, in addition to your password.
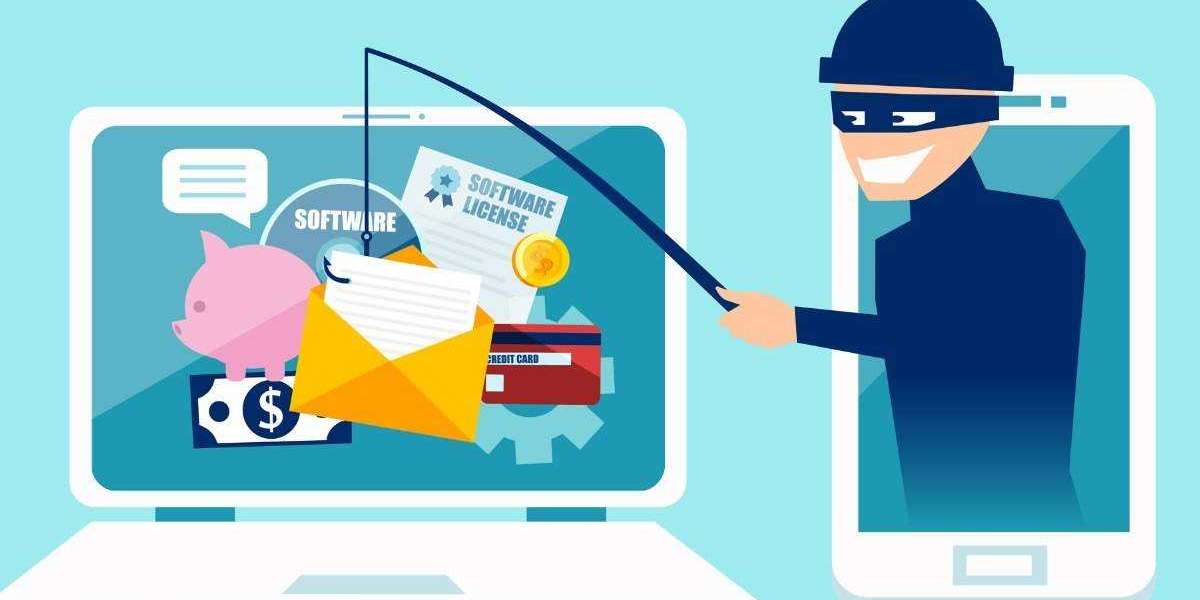
Be cautious of phishing attempts: Scammers often send deceptive emails, messages, or calls impersonating reputable organizations to trick you into revealing sensitive information. Be skeptical of unexpected communications and avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
Verify website security: Before entering personal or financial information on a website, ensure it has a secure connection. Look for "https://" in the URL, along with a padlock symbol, which indicates that the site has an SSL certificate and encrypts data transmitted between your browser and the server.
Stay updated with software and security patches: Keep your operating system, web browser, antivirus software, and other applications up to date. Regularly install security patches and updates to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Be cautious with public Wi-Fi: Avoid accessing sensitive information or making financial transactions when connected to public Wi-Fi networks. If you need to do so, use a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your connection and protect your data.
Research and verify investment opportunities: Be skeptical of too-good-to-be-true investment offers promising high returns with little risk. Research and verify the legitimacy of investment opportunities and consult with a trusted financial advisor before making any financial commitments.
Be vigilant about online purchases: When shopping online, only use reputable websites and ensure the payment process is secure. Read reviews, verify the seller's credibility, and be cautious when providing your credit card information.
Educate yourself: Stay informed about the latest online scams and techniques used by scammers. Be skeptical, trust your instincts, and if something seems suspicious, report it to the appropriate authorities.
Remember, online scams can evolve and become more sophisticated, so it's important to stay vigilant, trust your instincts, and prioritize your online security at all times.
How to identify scammers?
Identifying scammers can be challenging since they can be quite deceptive. However, here are some common signs that can help you identify potential scammers:
Unsolicited contact: Scammers often initiate contact through unsolicited emails, phone calls, text messages, or social media messages. They may claim to be from a reputable organization or government agency. Be cautious if you didn't initiate contact or if the communication seems unexpected or out of the blue.
Pressure and urgency: Scammers often create a sense of urgency or pressure to rush you into making quick decisions. They may claim that you're in immediate danger or offer limited-time offers that require immediate action. Legitimate organizations typically give you time to think and make informed decisions.
Request for personal or financial information: Be wary of anyone who asks for your personal or financial information, such as your social security number, bank account details, credit card information, or passwords. Legitimate organizations rarely ask for such information through unsolicited communication.
Poor grammar and spelling: Many scams originate from non-native English speakers or countries where English is not the primary language. Pay attention to emails or messages with poor grammar, spelling errors, or awkward sentence structures. However, note that not all scammers have poor language skills, so this alone is not a definitive indicator.
Suspicious URLs or email addresses: Scammers often use URLs or email addresses that mimic legitimate websites or organizations. Carefully examine the email address or URL for any slight variations or misspellings. Hover over links without clicking to see the actual destination in the status bar of your browser.
Too-good-to-be-true offers: Scammers may promise extraordinary returns, exclusive deals, or guaranteed winnings. If an offer sounds too good to be true, it probably is. Be cautious of schemes that promise quick wealth or benefits that seem unrealistic.
Payment requests via unconventional methods: Scammers may insist on unusual payment methods like wire transfers, prepaid gift cards, or cryptocurrency. Legitimate organizations typically offer more traditional and secure payment options.
Lack of verifiable information: Scammers often avoid providing verifiable information about themselves or their organization. They may be evasive when asked for details or provide vague answers. Legitimate businesses are usually transparent and readily share information about their company.
High-pressure sales tactics: Scammers often use aggressive sales tactics to manipulate you into making impulsive decisions. They may use fear, intimidation, or flattery to convince you to take immediate action without considering the consequences.
Trust your instincts: If something feels off or doesn't seem right, trust your instincts. If you have doubts or suspicions about a person, offer, or situation, take a step back, do some research, and seek advice from trusted friends, family, or professionals.
Remember, scammers are constantly evolving their techniques, so it's important to stay informed, skeptical, and cautious when dealing with unsolicited requests or offers. When in doubt, it's better to err on the side of caution and protect your personal and financial information.