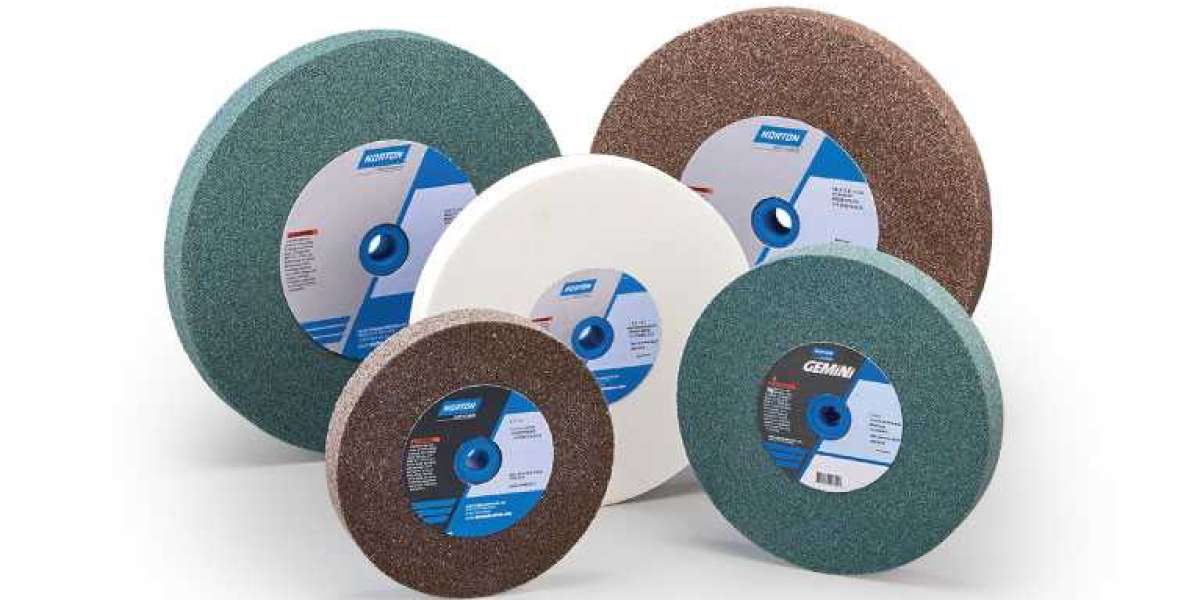
Grinding wheels are a crucial tool in various industries, from metalworking to woodworking, for material removal and surface finishing. Understanding the different types of abrasives used in grinding wheels can help you select the best wheel for your specific application.
The most common types of grinding wheel abrasives used in grinding wheels are aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, and ceramic. Each has unique properties that make them suitable for different applications.
Aluminum oxide is the most commonly used abrasive in grinding wheels. It is durable, versatile, and can be used on a wide range of materials, including steel, iron, and non-ferrous metals. Aluminum oxide is also ideal for grinding hard materials, such as cemented carbides.
Silicon carbide is a harder and more brittle abrasive than aluminum oxide. It is ideal for grinding harder materials, such as ceramics, glass, and cast iron. Silicon carbide is also used for non-ferrous metals and low-tensile strength materials.
Ceramic abrasives are the newest type of abrasive used in grinding wheels. They are made from a mix of aluminum oxide and ceramic grains, which makes them extremely durable and resistant to wear. Ceramic abrasives are ideal for grinding hard materials at high speeds and with heavy pressures.
When selecting a grinding wheel, it is essential to choose the right abrasive for your application. Factors to consider include the type of material being ground, the desired surface finish, and the level of precision required. Consult with a grinding wheel manufacturer or supplier to determine the best abrasive for your specific application.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of abrasives used in grinding wheels can help you choose the right wheel for your application. Whether you are working with steel, ceramics, or other materials, selecting the appropriate abrasive is crucial for achieving the desired results.