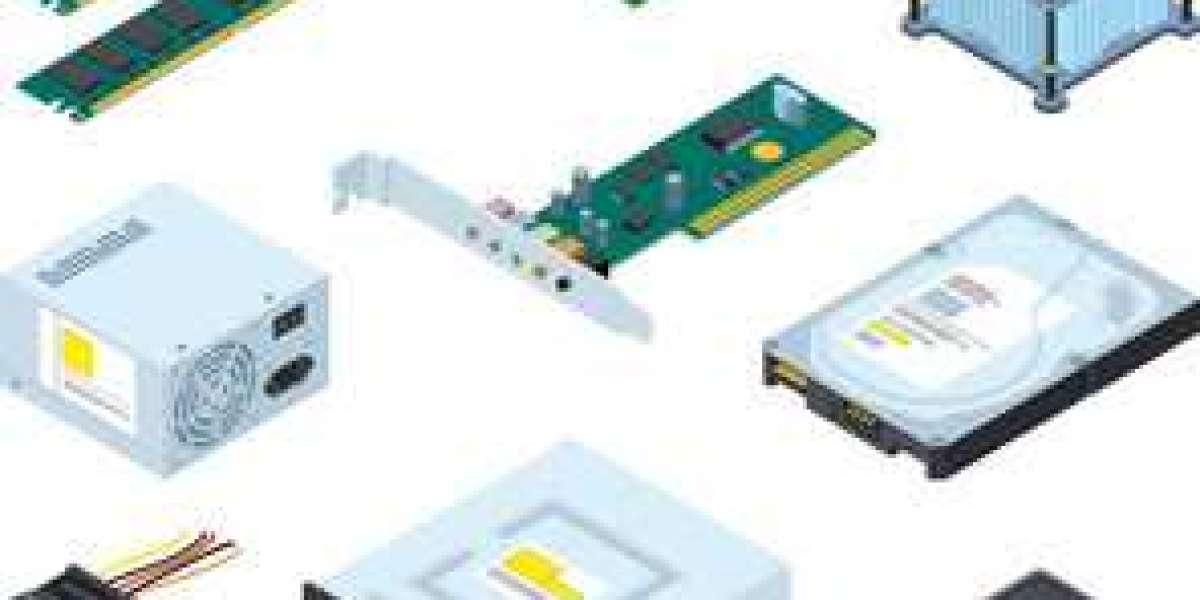
Computer hardware components are the physical parts of some type of computer system that enable it to operate and perform various tasks. These components include the central processing unit (CPU), motherboard, memory (RAM), storage devices, graphics processing unit (GPU), power supply unit (PSU), peripherals, and networking hardware The CPU is frequently referred to as the brain of the computer, in charge of executing instructions, performing calculations, and managing data processing tasks. It contains components such as the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit, which interact to hold out operations.
The motherboard serves as the central hub of the computer, connecting all the hardware components. It provides interfaces for the CPU, memory modules, storage devices, and expansion cards, facilitating communication between these components. The motherboard also houses essential components such as the chipset and BIOS, which manage system initialization and data flow Memory modules, commonly referred to as RAM (Random Access Memory), provide temporary storage for data and instructions that the CPU needs to get into quickly. RAM modules store data temporarily while the computer is powered on, enabling fast read and write operations. The amount and speed of RAM installed in a method significantly impact its performance, especially when running memory-intensive tasks.
Storage devices, such as hard disk drive drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs), are in charge of storing data permanently or semi-permanently. HDDs use spinning magnetic disks to store data, while SSDs employ flash memory technology for faster access and transfer speeds. External storage devices like USB flash drives and external hard disks offer convenient options for expanding storage capacity and transferring data between devices Graphics processing units (GPUs) are specialized hardware components in charge of rendering images and videos on computer displays. GPUs master parallel processing tasks needed for graphics-intensive applications such as gaming, video editing, and 3D modeling. Modern GPUs feature tens of thousands of processing cores optimized for parallel computation, enabling high-performance graphics rendering and accelerating tasks like machine learning and scientific simulations 0R5P25 .
The power supply unit (PSU) converts AC power from the electrical outlet into DC power required by computer components. It delivers stable and reliable power to all hardware components, ensuring proper operation and preventing damage from power fluctuations. PSU wattage and efficiency ratings are very important considerations when selecting a power, while they determine the maximum power output and energy efficiency of the system Peripherals such as for instance keyboards, mice, monitors, printers, and speakers complement the core hardware the different parts of some type of computer system, enhancing usability and functionality. Peripherals enable users to communicate with and input data to the computer, display output, and perform specific tasks such as for instance printing documents or hearing audio.
Networking hardware components enable computers to communicate and connect to local networks or the internet. Network interface cards (NICs) or network adapters facilitate wired or wireless connections between computers and network devices. Routers, switches, and modems serve as intermediary devices that manage data traffic and enable communication between multiple devices on a network. Additionally, wireless access points provide wireless connectivity to devices in just a specific area, allowing for seamless connectivity in homes, offices, and public spaces.