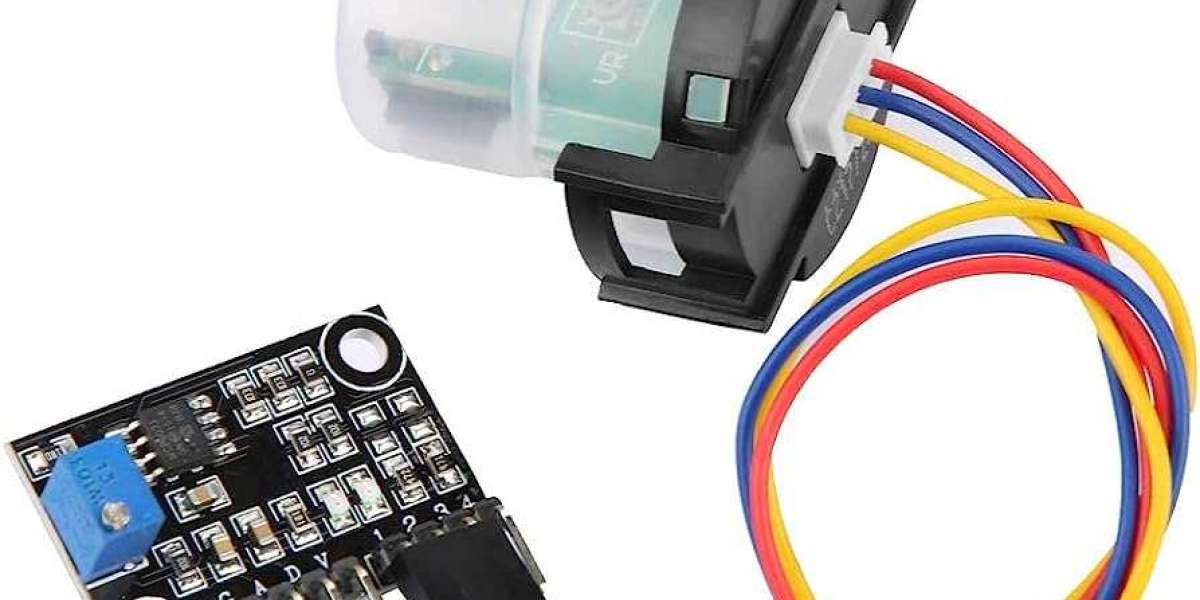
An ultrasonic distance sensor is a versatile device used for measuring distances between the sensor and an object without physical contact. It utilizes ultrasonic waves to perform this task. The sensor typically consists of two main components: a transceiver and a controller.
When the sensor is activated, the transceiver emits high-frequency ultrasonic waves, usually in the range of 40 kHz to 200 kHz, depending on the model. These waves travel through the air and propagate towards the target object. When the ultrasonic waves encounter an object in their path, they reflect back towards the sensor.
The sensor's controller then measures the time it takes for the ultrasonic waves to travel from the sensor to the object and back. Since the speed of sound in air is constant, the controller can calculate the distance by applying the formula: Distance = (Speed of Sound * Time of Flight) / 2. Dividing the time by two accounts for the round-trip journey of the ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasonic distance sensors are widely used in various applications, such as robotics, automotive parking assistance, industrial automation, and even in smartphones for proximity sensing. They offer non-contact distance measurements, which makes them suitable for applications where physical contact is undesirable or unfeasible. Additionally, their accuracy, simplicity, and relatively low cost have made them a popular choice in the field of distance sensing technology.